Benchmark of the iFigure: Evaluation of Answer Quality on Minecraft
Introduction
This paper presents a benchmark study of the iFigure AI agent aimed at evaluating its ability to accurately answer questions related to the video game Minecraft. The primary objective of the study was to assess the extent to which Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) and a generation control mechanism (PWG) influence the accuracy of responses produced by a large language model.Methodology
Model Configuration
The same model configuration was used consistently across all experimental conditions, with no architectural
modifications.
Dataset
The evaluation was conducted using the publicly available dataset:
This dataset contains several hundred thousand question-answer pairs related to game mechanics, items, and rules
in
Minecraft.
From this dataset, 199 questions were randomly selected for benchmarking.
Search System
To implement Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), the Kavunka search engine was used.
Indexing characteristics:
- The website https://minecraft.wiki/ was maximally indexed
- More than 8,000 pages were included in the index
- The agent had access exclusively to this source
Thus, when RAG was enabled, the model relied solely on the official wiki-based knowledge
repository.
Experimental Setup
Three independent experimental configurations were evaluated:
-
1. Without RAG and PWG
- No search queries were performed
- Responses were generated exclusively based on the internal knowledge of the language model
-
2. With RAG, Without PWG
- The agent queried the Kavunka search engine
- Retrieved information was incorporated into responses
- No generation constraints were applied
-
3. With RAG and PWG
- Search functionality was enabled
- The PWG (Permitted Word Generation) mechanism was applied
- The generation of unreliable or unauthorized formulations was restricted
Evaluation Metric
Response quality was assessed using the following metric:
BERT F1 (bert_f1_rank)
This metric measures semantic similarity between the model-generated answer and the
reference answer.
Value interpretation:
All responses were sorted from highest to lowest BERT F1 score (left to right).
- 1.0 — near-complete semantic equivalence
- ≥ 0.9 — correct answer
- < 0.9 — partially or fully incorrect answer
Experimental Results
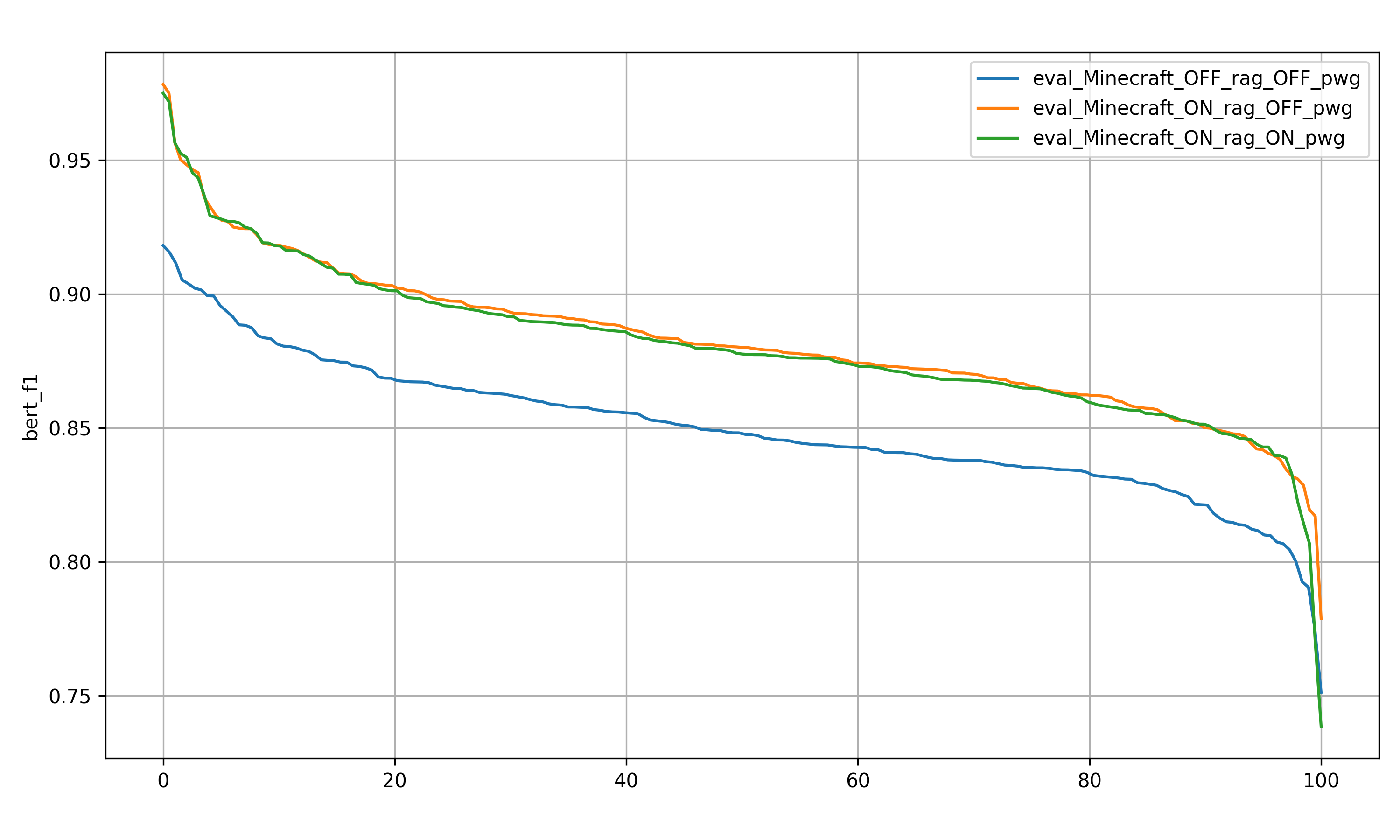
The resulting graph contains three curves:
- Blue line — without RAG and PWG
- Orange line — with RAG, without PWG
- Green line — with RAG and PWG
General Observations
Model Without RAG
- Significantly lower average BERT F1 scores
- Rapid decline in response quality
- Large number of answers below the 0.9 correctness threshold
Model With RAG
- Substantial increase in accuracy
- Majority of responses above 0.9
- Smoother decline curve
RAG + PWG
- Performance closely mirrors standard RAG
- No significant metric improvement observed
- Slightly more stable behavior toward the lower-performing tail
Analysis
Impact of RAG
The use of Retrieval-Augmented Generation resulted in a substantial improvement in response quality:- Increased number of correct answers
- Reduced hallucination rate
- Greater reliance on verified external sources
Impact of PWG
Within the scope of this benchmark, the PWG mechanism:- Did not produce a measurable increase in BERT F1
- Did not significantly alter the overall curve shape
- Reduces confidently incorrect responses
- More frequently signals uncertainty to the user
- Decreases the likelihood of fabricated facts
Conclusions
The benchmark results support the following conclusions:
1. RAG Significantly Improves Accuracy
In this experiment:- No statistically significant accuracy gain was observed
- Differences compared to standard RAG were minimal
3. The LLM + RAG Combination Is Optimal
The architecture combining:- LLM + search index + RAG
Final Remarks
This benchmark demonstrates that the iFigure AI agent substantially improves response
quality when leveraging an external knowledge base.
Key findings:
- Without RAG — limited accuracy
- With RAG — high correctness rate
- RAG + PWG — safer and more controlled agent behavior